[Design Pattern] 싱글톤 패턴
싱글턴 패턴
정의
하나의 인스턴스만을 가지는 class의 집합
static 키워드를 사용하여 구현 가능
메서드 실행 주체
클래스가 수행하는 메서드 → static
인스터스가 실행 → 일반
예제: 로그 출력기 만들기
의도: 모든 회원들의 입출금 내역을 파일에 저장
- 계좌 클래스
public class Account {
private int balance;
private String owner;
private Logger myLogger;
public Account(String owner, int balance){
this.balance = balance;
this.owner = owner;
this.myLogger = new Logger();
}
public String getOwner(){
return owner;
}
public int getBalance(){
return balance;
}
public void deposit(int money){
myLogger.log("owner"+" : "+this.getOwner()+" deposit "+money);
balance+=money;
}
public void withdraw(int money){
if(balance >=money){
myLogger.log("owner"+" : "+this.getOwner()+" withdraw "+money);
balance-=money;
}
}
}
- 로그 출력기 클래스
import java.util.Date;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class Logger{
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
public Logger(){
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
}catch (IOException e){}
}
public void log(String message){
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date data = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(data)+ " : " + message);
}
}
<문제점>
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acct1 = new Account("Wuhan",1000000);
acct1.deposit(20000);
Account acct2 = new Account("YongGang",20000);
acct2.withdraw(20000);
}
}
해당 코드 실행시 뒤에 결과로인해 앞에 결과가 덮어 씌어짐으로 사용자의 모든 입출력이 찍히는 의도가 작동되지 않음 즉 본래의 의도와 벗어남
(해결책) 싱글톤 패턴으로 수정한 출력기 클래스들
Eager Initialization
이른 초기화: 인스턴스를 프로그램이 시작되자 마자 미리 생성
문제점: 클래스 로딩 시점에 초기화되어 인스턴스가 필요하지 않은 경우에도 생성
import java.util.Date;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class Logger{
private static Logger instance = new Logger();
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private static PrintWriter writer;
private Logger(){
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
}catch (IOException e){}
}
public static Logger getInstance(){
return instance;
}
public void log(String message){
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date data = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(data)+ " : " + message);
}
}
Lazy Initialization
늦은 초기화: Eager Initialization의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 인스턴스가 필요할 때 생성하는 방식
문제점: 다중 스레드 환경에서는 단일 인스턴스 생성이라는 싱글톤의 목적과는 다르게 여러 인스턴스가 생성될 위험이 있음
import java.util.Date;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class Logger{
private static Logger logger;
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private static PrintWriter writer;
private Logger(){
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
}catch (IOException e){}
}
public static Logger getInstance(){
if(logger==null)
logger = new Logger();
return logger;
}
public void log(String message){
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date data = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(data)+ " : " + message);
}
}
<문제점 예시>
import java.util.Random;
class User extends Thread{
public User(String name){super(name);}
public void run(){
Random r = new Random();
Account acct = new Account(Thread.currentThread().getName(), r.nextInt(1000000));
if(r.nextBoolean()) acct.withdraw(r.nextInt(acct.getBalance()));
else acct.deposit(r.nextInt(acct.getBalance()));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User[] users = new User[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
users[i] = new User("suhan"+i);
users[i].start();
}
}
}코드 실행 결과
Logger@6ba60d46
Logger@3b1b95ed
Logger@1e628db7
Logger@70282c99
Logger@6a07b062
Logger@148cd591
Logger@7f20d3a2
Logger@71eac517
Logger@f37a491
Logger@33306c50
해결책: synchronized 키워드
synchronized 키워드 사용: instance를 임계구역으로 설정 한다면 다중 스레드 환경에서의 문제점을 해결 할 수 있다.
문제점: 비용이 비싸다 제일 처음에만 synchronized로 임계구역으로 설정한게 필요하지 그 이후 부터는 공유자원으로 보호 하지 않아도 되기 때문에 비효율적인 방식이 되어 버린다.
public class Logger{
private static Logger instance;
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private static PrintWriter writer;
private Logger(){
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
}catch (IOException e){}
}
synchronized public static Logger getInstance(){
if(instance==null) instance = new Logger();
return instance;
}
public void log(String message){
System.out.println(this.toString());
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date data = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(data)+ " : " + message);
}
}
해결책: DCL(Double Check Locking)
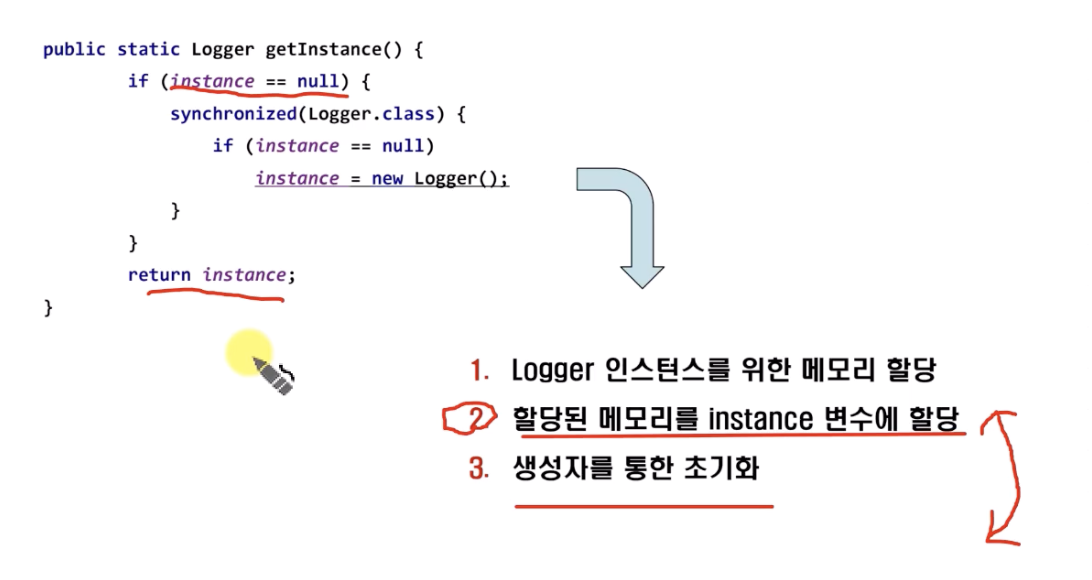
임계구역(Critical Section)에 진입하기 전에 두 번의 검사를 수행하여 해당 객체가 이미 생성되었는지 확인하는 방법 synchronized 키워드 문장을 실행사기 전에 조건문을 사용하여 특정 조건이 수행되지 않았는지 체크하고 임계구역으로 설정한다.
문제점: DCL 방식을 사용하더라도 생성자를 통한 초기화를 하기 전 인스턴스에 접근 하는 문제가 발생 할 수 있다
+ 단 Logger instance 를 volatile 키워드를 사용하여 순서 변경을 막는다면 문제점이 없다.
해결책: Initialization on demand holder idiom
내부 클래스로 만들어 해당 클래스를 통해 인스턴스를 반환함으로서 위에서 발생 할 수 있는 생성자를 통한 초기화를 하기 전 인스턴스에 접근 하는 문제 해결
참조 하기 전 (메모리 적재 x) -> 참조 후 (메모리 적재) 내부 클래스임으로 바로 생성 (원자적 행위)임으로 끼어들기 불가능
import java.util.Date;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class Logger{
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private static PrintWriter writer;
private Logger(){
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
}catch (IOException e){}
}
private static final class LoggerHolder {
private static final Logger instance = new Logger();
}
public static Logger getInstance(){
return LoggerHolder.instance;
}
public void log(String message){
System.out.println(this.toString());
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date data = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(data)+ " : " + message);
}
}
내용 요약
- when: 단일 인스턴스로만 특정 클래스가 필요한 상황
- how: static 키워드를 통해 정적 요소 생성 반환, private 접근 지정자로 생성자 외부 호출로 부터 보호
- solve: 늦은 초기화(lazy initialization)을 활용하여 정적으로 클래스 본인 자체를 내부에 생성하고 호출시 처음 딱 한번 생성시키고 반환, 내부 클래스를 통해 로딩시 바로 해당 인스턴스가 생성되도록 구현
class SingleThon {
// 생성자 private 접근 지정자로 외부 호출 제어
private SingleThon(){}
/*
그 밖에 맴버 변수 함수들..
*/
private static final class InstanceHolder{
private static final SingleThon instance = new SingleThon();
}
// 처음 호출 시 딱 한번만 생성되고 그 이후는 기존에 있던 인스턴스 반환
public static SingleThon getInstance(){
return InstanceHolder.instance;
}
}